AI Functions in SQL - Revolutionizing Data Analysis
The adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in enterprise environments is often associated with complex projects, specialized teams, and custom developments. However, Databricks has simplified this process by integrating AI Functions directly into SQL, allowing analysts and data engineers to apply AI capabilities to their data without leaving the lakehouse.
With these functions, tasks such as translation, sentiment analysis, classification, or summary generation become as simple as executing a SQL query.
What are AI Functions?
AI Functions are built-in functions in Databricks that enable the use of AI models directly from SQL, Notebooks, and production pipelines.
This means that AI runs in the same place where data lives, eliminating the need to move information to external systems and reducing friction in the workflow.
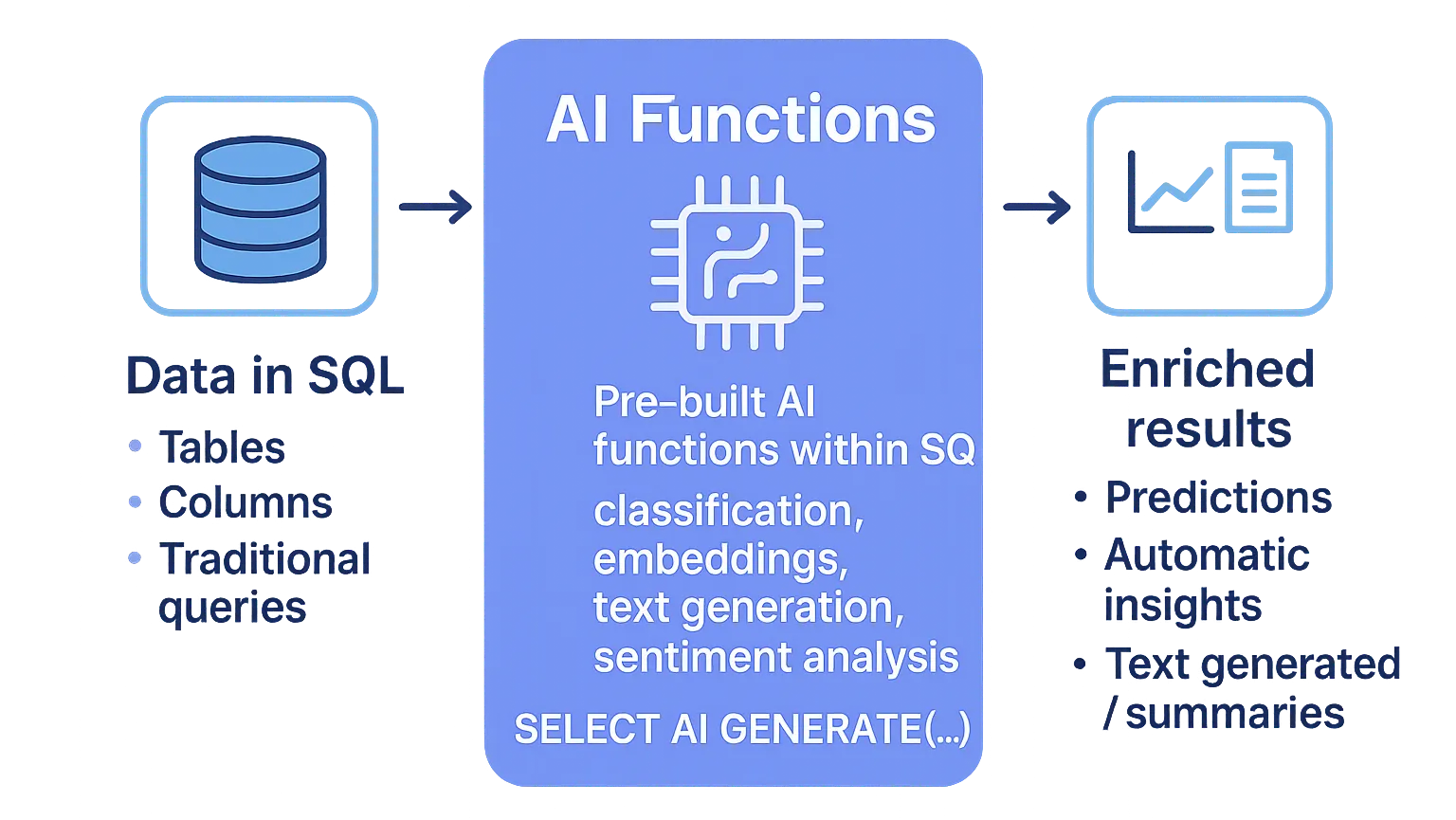
Main advantages:
- Accessibility
- Scalability
- Flexibility
- Monitoring
Accessibility
AI Functions democratize access to artificial intelligence by eliminating traditional technical barriers.
- Native SQL: They run directly as standard SQL functions without additional APIs
- Zero-shot learning: They don’t require prior training or model configuration
- Universal compatibility: They work in SQL warehouses, Python/Scala notebooks, and Delta Live Tables pipelines
- Intuitive syntax:
SELECT ai_summarize(text) FROM tableis as simple as any built-in SQL function
Scalability
Designed to automatically scale from prototypes to enterprise production workloads.
- Distributed processing: Leverage Databricks’ distributed architecture to process millions of rows
- Auto-scaling compute: Clusters automatically adjust according to inference demand
- Batch and streaming: Compatible with Delta Live Tables for continuous and batch processing
- Lakehouse architecture: Process data directly in Delta Lake without data movement
Flexibility
They offer multiple model options and configurations to adapt to different business needs.
- Foundation models: Direct access to Llama 3.1, Mixtral, DBRX and other state-of-the-art models
- External models: Integration with OpenAI GPT, Anthropic Claude, and other providers via Model Serving
- Custom models: Deploy your own fine-tuned models using Mosaic AI Training
- Governance: Granular control of permissions and usage policies per workspace and user
Monitoring and Observability
Complete telemetry and governance system integrated in Unity Catalog for maximum operational control.
- Usage tracking: Detailed metrics of request volume, latency and token consumption per model
- Cost management: Real-time cost dashboards with configurable budget alerts
- Audit logs: Complete record in Unity Catalog of all invocations and results
- MLflow integration: Automatic tracking of experiments and model lineage for compliance
Accessibility
AI Functions democratize access to artificial intelligence by eliminating traditional technical barriers.
- Native SQL: They run directly as standard SQL functions without additional APIs
- Zero-shot learning: They don’t require prior training or model configuration
- Universal compatibility: They work in SQL warehouses, Python/Scala notebooks, and Delta Live Tables pipelines
- Intuitive syntax:
SELECT ai_summarize(text) FROM tableis as simple as any built-in SQL function
Scalability
Designed to automatically scale from prototypes to enterprise production workloads.
- Distributed processing: Leverage Databricks’ distributed architecture to process millions of rows
- Auto-scaling compute: Clusters automatically adjust according to inference demand
- Batch and streaming: Compatible with Delta Live Tables for continuous and batch processing
- Lakehouse architecture: Process data directly in Delta Lake without data movement
Flexibility
They offer multiple model options and configurations to adapt to different business needs.
- Foundation models: Direct access to Llama 3.1, Mixtral, DBRX and other state-of-the-art models
- External models: Integration with OpenAI GPT, Anthropic Claude, and other providers via Model Serving
- Custom models: Deploy your own fine-tuned models using Mosaic AI Training
- Governance: Granular control of permissions and usage policies per workspace and user
Monitoring and Observability
Complete telemetry and governance system integrated in Unity Catalog for maximum operational control.
- Usage tracking: Detailed metrics of request volume, latency and token consumption per model
- Cost management: Real-time cost dashboards with configurable budget alerts
- Audit logs: Complete record in Unity Catalog of all invocations and results
- MLflow integration: Automatic tracking of experiments and model lineage for compliance
Types of AI Functions
Databricks has designed an AI Functions ecosystem that is strategically divided into two complementary categories, each optimized for different usage patterns and levels of customization. This dual architecture allows both rapid implementation of common use cases and maximum flexibility for specific business requirements.
There are two main categories:
1. Task-specific functions
These are ready-to-use functions, designed to solve common business problems without the need to configure models. Some of the most used are:
ai_analyze_sentiment()→ Detects sentiment (positive, negative, neutral) in text.ai_classify()→ Classifies text into predefined categories.ai_fix_grammar()→ Corrects grammatical errors in text.ai_summarize()→ Generates automatic summaries.ai_translate()→ Translates to different languages.ai_forecast()→ Performs forecasts on time series.
These functions are recommended for users looking for fast and consistent results.
2. General purpose function: ai_query()
It is the most flexible function, as it allows performing custom queries to language models. With it you can use:
- Foundation models hosted by Databricks, such as Llama 3 or Gemma.
- Own models deployed in Mosaic AI Model Serving.
- External models connected via compatible endpoints.
Practical examples
AI Functions shine when applied to real use cases. Below, we explore implementations that demonstrate how these functions can transform everyday business operations, from feedback analysis to content automation.
Sentiment analysis on customer reviews
Case: Process customer feedback to identify satisfaction patterns.
-- Basic sentiment analysis
SELECT
review_id,
review_text,
ai_analyze_sentiment(review_text) AS sentiment,
ai_summarize(review_text) AS summary
FROM customer_reviews
WHERE created_date >= current_date() - 7
ORDER BY review_id;
-- Example result:
-- sentiment can be: 'positive', 'negative', 'neutral', 'mixed'Automatic content classification
Case: Automatically categorize support tickets by department and urgency.
-- Ticket classification using ai_classify
SELECT
ticket_id,
description,
ai_classify(description, array('technical', 'billing', 'general_inquiry')) AS department,
ai_classify(description, array('low', 'medium', 'high', 'urgent')) AS priority
FROM support_tickets
WHERE status = 'open';Automatic product translation
Case: Translate product descriptions for international markets.
-- Translation to multiple languages
SELECT
product_id,
description_en,
ai_translate(description_en, 'Spanish') AS descripcion_es,
ai_translate(description_en, 'French') AS description_fr,
ai_translate(description_en, 'German') AS beschreibung_de
FROM product_catalog;Custom queries with ai_query()
Case: Structured information extraction using foundation models.
-- Using Llama 3.3 model for custom analysis
SELECT
customer_id,
feedback_text,
ai_query(
"databricks-meta-llama-3-3-70b-instruct",
"Extract the main complaint and suggested solution from this customer feedback: " || feedback_text
) AS analysis
FROM customer_feedback
LIMIT 10;Grammar correction in content
Case: Improve the quality of user-generated content.
-- Automatic grammar correction
SELECT
post_id,
original_content,
ai_fix_grammar(original_content) AS corrected_content
FROM user_posts
WHERE language = 'en';Semantic search with vector_search
Case: Find similar documents using vector search.
-- Vector index search (requires configured Mosaic AI Vector Search)
SELECT
vector_search(
index => 'catalog.schema.document_index',
query => 'artificial intelligence machine learning',
num_results => 5
) AS similar_documents;Content generation with ai_gen
Case: Automatically create product descriptions.
-- Content generation
SELECT
product_name,
category,
ai_gen("Write a compelling 2-sentence product description for: " || product_name || " in category: " || category) AS generated_description
FROM products
WHERE description IS NULL;Enterprise use cases
AI Functions allow addressing a wide range of needs:
Customer Experience
Review analysis, spam detection or automatic classification of support tickets.
Finance
Legal and compliance
Operations
Scalability and production operation
One of Databricks’ greatest strengths is that these functions are not only designed for testing, but also for production environments.
They can be integrated into:
- Lakeflow declarative pipelines.
- Batch and streaming processing.
- Production workflows with metrics monitoring.
Additionally, Databricks offers usage and cost dashboards, facilitating the management of expenses associated with model inference.
Conclusion
AI Functions in SQL represent a decisive step towards the democratization of AI in the data world. By integrating advanced language model capabilities directly into the Databricks ecosystem, any analyst or engineer can enrich their analysis without leaving the SQL environment.
This not only accelerates experimentation, but also enables real production use cases with scalability and cost control. Ultimately, it is a tool that brings the power of AI to the day-to-day operations of organizations.