
Generative AI Solution Development
- Juan Diaz
- Apr 30, 2025
- 08 Mins read
- Databricks
Generative AI refers to a category of artificial intelligence that can generate text, images, code, audio, and other content formats based on input data or prompts. It leverages powerful machine learning models known as foundation models, which are pre-trained on massive datasets and can be fine-tuned for a wide range of specific tasks.
One of the most prominent types of foundation models are large language models (LLMs). These models are capable of understanding and generating human-like language. Tools like ChatGPT, Claude, and models from Hugging Face or Meta are examples of LLMs.
In the context of Databricks, generative AI is used to accelerate data tasks, improve user interaction through natural language, and create intelligent assistants or applications. This blog post explores how Databricks helps you get started through their Generative AI Solution Development course and practical labs.
Databricks offers an amazing resource called Databricks Academy, which features a variety of courses and labs designed to help users learn about the platform and its capabilities. In this article, we’ll dive into the Generative AI Solution Development course, which is a hands-on lab that introduces the fundamentals of generative AI and how it can be applied to real-world scenarios.
Illustration representing Generative AI capabilities — Image by Seanprai S. on Vecteezy
Prompt Engineering Primer
Basics…
To start, let’s cover the basics of prompt engineering. Prompt engineering refers to the process of designing and refining prompts to optimize the response from a language model (LM). It’s all about crafting prompts that guide the model toward producing relevant and accurate responses.
- Prompt: The input or query given to the language model to elicit a response.
- Prompt engineering: The practice of designing and refining prompts to optimize the response from the model.
Prompt Components
Here are the main components of a prompt:
- Instruction: The task or question you want the model to address.
- Context: Additional information or background to help the model better understand the task.
- Input: The specific data or examples given to the model to assist in generating the response.
- Output: The expected result or response generated by the model.
Prompt Engineering Techniques
Now, let’s explore several techniques for prompt engineering that can help improve model performance. In this blog, we’ll cover some of the most common techniques you can start using.
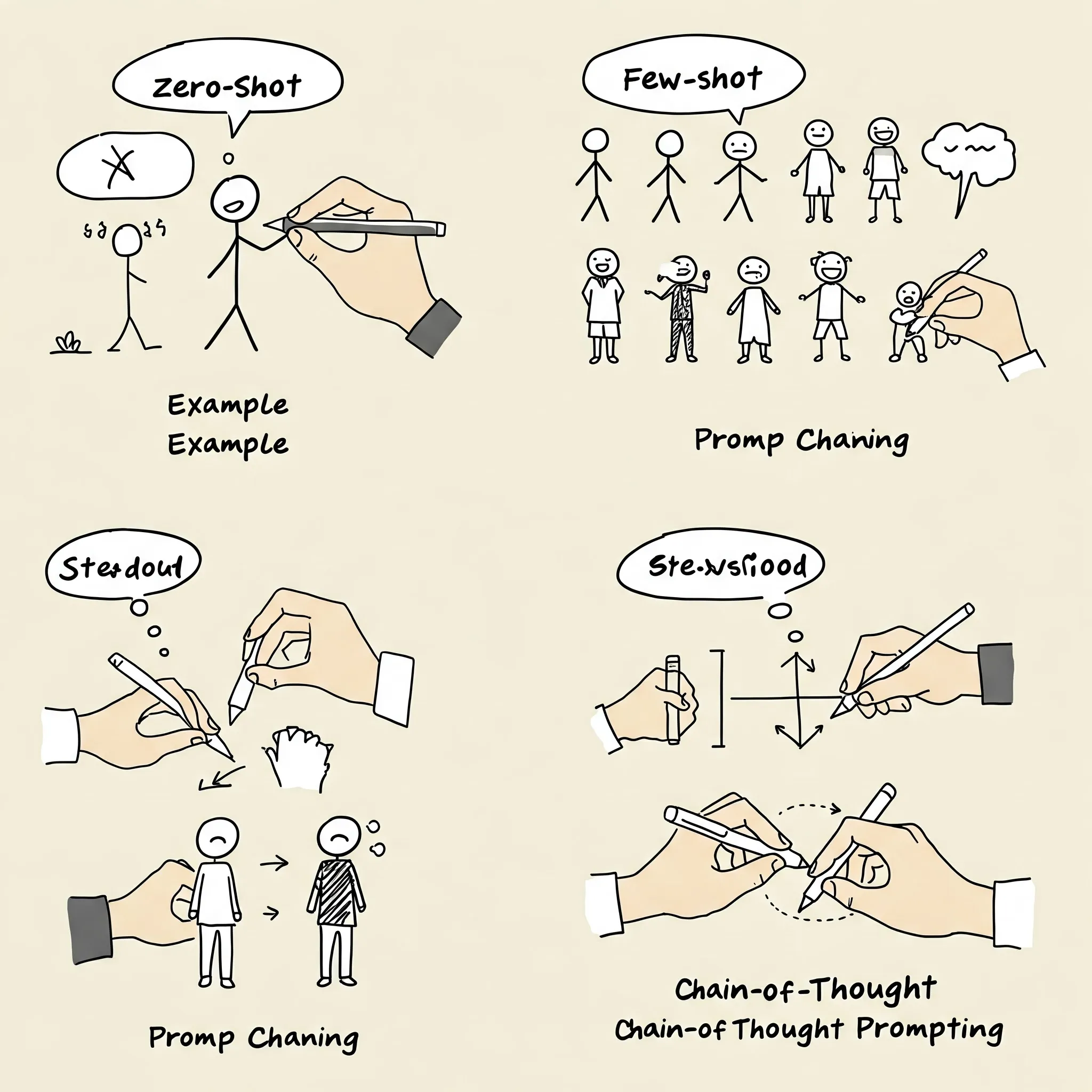
Zero-shot / Few-shot Prompting
-
Zero-shot prompting: You give the model a task with no examples. The model relies on its pre-existing knowledge to generate a response. Here is a simple prompt example:
Translate the following English sentence to Spanish: ‘Hello, how are you?’
Write a Databricks SQL query that analyzes customer data.
-
Few-shot prompting: You provide the model with a few examples of the task you want it to perform. Here is a prompt example: Here’s a simpler few-shot prompting example related to Databricks:
Write a Databricks SQL query. Here are some examples:
- A query that counts daily active users from the events table.
- A query that calculates average purchase value by customer segment.
- A query that identifies the top performing products by region.
Prompting Chaining
Prompting chaining involves breaking a complex task into smaller, manageable steps. This helps the model focus on each step and generate more accurate responses. Here is an example:
Initial Prompt:
You are a Data Engineer expert. Write a summary for my blog about how to use Databricks Community Edition.
Follow-up Prompt:
Great! Now write an introduction based on this summary.
Follow-up Prompt:
Excellent. Now expand this into a section titled “Why use Databricks Community Edition?”
And continue with separate prompts for each subsequent section.
Chain-of-Thought Prompting
Similar to prompting chaining, chain-of-thought prompting asks the model to explain its reasoning or thought process at each step. This improves the quality and accuracy of the responses. If you want the model to solve a math problem, you might ask it to explain its reasoning at each step. For example:
If Susan is 5 years older than John, and John is 10 years old, how old is Susan? Let’s think step by step to solve this problem.
I want to create a Delta Live Table pipeline in Databricks. Let’s think step by step.
Prompt Engineering Tips and Tricks
Prompts are model-specific
Different models may respond differently to the same prompt. It’s important to experiment with different prompts and techniques to find what works best for your specific use case.
- Different models may require different prompt formats.
- Different use cases may benefit from different prompt styles.
- Each model has its own strengths and weaknesses.
- Iterative development is key—test, tweak, and test again.
- Be aware of bias and hallucinations in the model’s responses.
Format prompts helps
Using a specific format for your prompts can help the model better understand the task and generate more accurate responses. For example:
- Use bullet points, numbered lists, or clear delimiters.
- Request structured output formats like: HTML, JSON or Markdown
Formatting both the prompt and expected response helps reduce ambiguity.
Guide the model for better responses
You can improve response quality by explicitly guiding the model:
-
Ask the model not to make things up. For example:
If you don’t know the answer, say you don’t know.
Avoid guessing. Be factual.
-
Ask the model to be concise/specific. For example:
Provide a concise answer in 2–3 sentences. Condense this explanation.
-
Avoid assumptions or sensitive info. For example:
Do not assume gender, age, or intent. Avoid asking for personal data like SSNs or phone numbers.
-
Encourage step-by-step reasoning. For example:
Think step by step.
Ask me questions one at a time and wait for my response.
Guide the model for better responses
Guide the model by specifying requirements, such as asking it to avoid assumptions or to be concise.
Benefits and Limitations of Prompt Engineering
Benefits
- Simple and efficient.
- Predictable results.
- Tailored output.
Limitations
- The output depends on the model used.
- Limited by pre-trained knowledge.
- May require multiple iterations.
- May require domain-specific knowledge.
Building Generative AI Applications in Databricks
Databricks provides a powerful, unified platform to build and deploy generative AI applications using your own data. Through Mosaic AI and native support for foundation models, developers can create sophisticated applications that go beyond one-shot prompts. This section introduces Databricks’ approach to building production-grade generative AI apps.
Patterns for Generative AI Apps
Databricks distinguishes between two core development patterns:
-
Monolithic Prompt Pattern: You send a carefully engineered prompt to a large language model (LLM) and receive a response. This is useful for simple tasks like summarization, rephrasing, or basic Q&A.
Example:
Summarize the following Databricks notebook on Delta Lake optimization.
-
Agent-Based Pattern: A more advanced system where an agent coordinates multiple tools—like a LLM, a retriever, and a tool executor—to complete multi-step tasks. This is suitable for more dynamic and interactive applications, such as AI copilots or autonomous data agents.
Example:
A user asks, “Generate a revenue report for the last quarter.” The system retrieves the right tables, builds SQL queries, and uses the LLM to narrate the findings.
These patterns can be implemented directly in notebooks using LangChain, LlamaIndex, or Semantic Kernel, all of which are supported in Databricks.
What is Mosaic AI?
Mosaic AI is Databricks’ solution for building and deploying production-ready generative AI applications at scale. It provides a complete suite of tools for working with foundation models, implementing retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), and managing large language model operations (LLMOps).
Why Mosaic AI matters
Traditional ML platforms weren’t designed for the unique needs of generative AI—such as handling unstructured data, integrating with foundation models, or managing continuous iteration on prompts and model behavior. Mosaic AI bridges that gap by offering:
- Seamless integration with open-source frameworks like LangChain and LlamaIndex.
- Native support for foundation models like LLaMA 2 and MPT, including model fine-tuning.
- Purpose-built observability and evaluation tools for tracking LLM performance.
- Security and governance features to help enterprises deploy responsibly.
Example: End-to-End Workflow with Mosaic AI
Suppose you want to build a support chatbot using your company’s internal documentation. Here’s how Mosaic AI would support you:
- Ingest unstructured data using Databricks notebooks and pipelines.
- Embed and store documents in a vector store.
- Use LangChain or LlamaIndex to connect the LLM with your knowledge base (RAG pattern).
- Deploy the application via an API or Streamlit app.
- Monitor the model’s responses using Mosaic AI Evaluation tools.
Components of Mosaic AI
Mosaic AI is made up of several tightly integrated components designed to support the full development lifecycle of generative AI applications:
- Mosaic AI Training: Allows for the fine-tuning of foundation models using parameter-efficient training methods like LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation), enabling customization with lower compute costs.
- Mosaic AI Model Serving: Provides a scalable infrastructure to serve foundation models via real-time APIs or batch processing.
- Mosaic AI Gateway: Acts as a unified interface to interact with multiple LLM providers or endpoints, making it easy to switch between hosted and third-party models.
- Mosaic AI Evaluation: Offers built-in tools to evaluate model outputs, detect hallucinations, and measure response quality using both automated metrics and human feedback.
- RAG and LangChain/LlamaIndex Integration: Mosaic AI supports RAG out of the box by enabling seamless integration with LangChain or LlamaIndex, allowing LLMs to retrieve context from your enterprise data sources.
Use Case: Automating Knowledge Base Support
Imagine an enterprise wants to create a smart assistant that answers technical support questions based on internal documentation:
- Fine-tune an open-source LLM on customer support tickets using Mosaic AI Training.
- Ingest product guides and system manuals using a pipeline that stores embeddings in a vector store.
- Connect the model to the data using LangChain + RAG for accurate document retrieval.
- Serve the assistant with Mosaic AI Serving, routing calls through Mosaic Gateway.
- Monitor and evaluate outputs using Mosaic Evaluation to ensure accurate, safe responses.
This workflow reduces support costs, enhances self-service, and keeps data governance centralized in your Databricks environment.
Introduction to RAG
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a powerful pattern that enhances the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) by connecting them to external data sources. Instead of relying solely on what the model learned during training, RAG enables it to retrieve relevant information from structured or unstructured documents at runtime, improving factual accuracy and reducing hallucinations.
Why RAG?
While LLMs are impressive in generating human-like language, they can struggle with providing accurate answers for domain-specific or time-sensitive topics. RAG addresses this limitation by combining:
- Retrieval: Searching for relevant context in a knowledge base, such as internal documentation, wikis, PDFs, or databases.
- Generation: Passing the retrieved content into the prompt to guide the LLM’s output.
This hybrid approach helps deliver more grounded and context-aware responses.
RAG in Databricks
Databricks provides a robust and scalable environment to implement RAG workflows using familiar tools:
- Ingest and preprocess unstructured data (e.g., product manuals, support tickets, blog posts) using notebooks and Delta pipelines.
- Embed and index the data in a vector store using models like BGE or OpenAI embeddings.
- Integrate with retrieval frameworks such as LangChain or LlamaIndex to build the retrieval pipeline.
- Pass context to the LLM (e.g., MPT, LLaMA 2) along with the user prompt to generate a response grounded in enterprise data.
Example Workflow: Databricks-Powered RAG System
- Use a notebook to load internal PDF documentation.
- Chunk and clean the text data using LangChain utilities.
- Generate embeddings using a supported model (OpenAI, Hugging Face, etc.).
- Store the embeddings in a vector database (e.g., FAISS, Chroma).
- Create a retrieval chain that searches for relevant chunks in response to a query.
- Pass retrieved context and the original prompt to an LLM via Databricks Model Serving or external API.
- Display the grounded, context-rich response in a chatbot or app.
Benefits of RAG in the Enterprise
- Boosts accuracy of LLM outputs by grounding them in current, verified data.
- Reduces risks of hallucinated or outdated responses.
- Keeps sensitive data private by controlling the source content.
- Enables dynamic responses even with smaller, fine-tuned models.
With Databricks, all stages of the RAG architecture—from ingestion and retrieval to generation and evaluation—can be developed and deployed within a secure, unified platform.
Resources: